early_param是一个
early_param代码如下:
/*
* NOTE: @fn is as per module_param, not __setup!
* I.e., @fn returns 0 for no error or non-zero for error
* (possibly @fn returns a -errno value, but it does not matter).
* Emits warning if @fn returns non-zero.
*/
#define early_param(str, fn) \
__setup_param(str, fn, fn, 1)
/*
* Only for really core code. See moduleparam.h for the normal way.
*
* Force the alignment so the compiler doesn't space elements of the
* obs_kernel_param "array" too far apart in .init.setup.
*/
#define __setup_param(str, unique_id, fn, early) \
static const char __setup_str_##unique_id[] __initconst \
__aligned(1) = str; \
static struct obs_kernel_param __setup_##unique_id \
__used __section(".init.setup") \
__aligned(__alignof__(struct obs_kernel_param)) \
= { __setup_str_##unique_id, fn, early }
struct obs_kernel_param {
const char *str;
int (*setup_func)(char *);
int early;
};
#define __initconst __section(".init.rodata")示例,如果early_param("kgdboc_earlycon", kgdboc_earlycon_init);,他会解析为:
__setup_param("kgdboc_earlycon", kgdboc_earlycon_init, kgdboc_earlycon_init, 1)
static const char __setup_str_kgdboc_earlycon_init[] __initconst __aligned(1) = "kgdboc_earlycon";
static struct obs_kernel_param __setup_kgdboc_earlycon_init
__used __section(".init.setup")
__aligned(__alignof__(struct obs_kernel_param))
= { __setup_str_gdboc_earlycon_init, kgdboc_earlycon, 1 }
//最终解压为:
static const char __setup_str_kgdboc_earlycon_init[] __section(".init.rodata") __aligned(1) = "kgdboc_earlycon";
static struct obs_kernel_param __setup_kgdboc_earlycon_init __used __section(".init.setup") __aligned(__alignof__(struct obs_kernel_param)) = {
"__setup_str_gdboc_earlycon_init",
kgdboc_earlycon,
1
}可以看到实际上最后会编译出两个变量:char字符串(被放在.init.rodata段)和结构体struct obs_kernel_param(被放在.init.setup)。 依据经验,这样的做法,一般不会直接的去调用,而是通过一个遍历该两部分section而统一处理所有这样声明的参数。那我们来看看,是哪里进行了处理,我们仅需使用grep搜索early_param 即可。我们观察到文件init/main.c中:
extern const struct obs_kernel_param __setup_start[], __setup_end[];这个结构体struct obs_kernel_param就是我们刚刚声明的一个early_param的同一结构体,并且发现是extern和start,end。根据上面section分析,经验可得,该引入的__setup_start与__setup_end,实际上应该是在link script中声明的,我们搜索可得到: 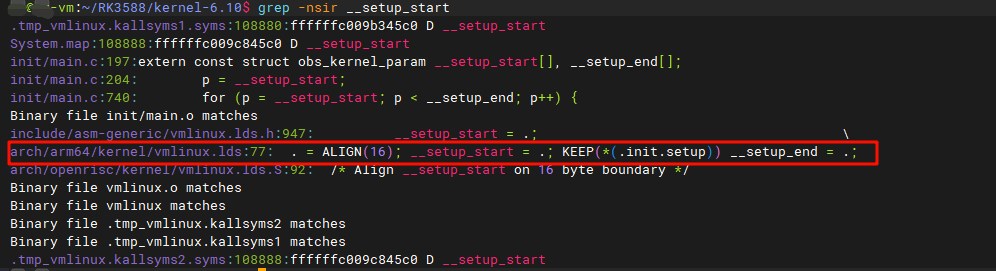
// arch/arm64/kernel/vmlinux.lds
.init.data : {
.....
. = ALIGN(16); __setup_start = .; KEEP(*(.init.setup)) __setup_end = .;
.....
}这段链接脚本大意是,所有的section .init.setup会被放在__setup_start与__setup_end之间。 题外:struct obs_kernel_param 中的obs表示的是obsolete,表示被抛弃,它一般仅留在代码中以兼容老的代码,但实际情况也没有去删除它。可以参考核心參數解析
接着,我们不得不需要提到command line机制,它的功能主要就是,在内核启动初期,有一些特定的函数需要执行,所以,我们从uboot区域传入一段command line,来控制部分代码段执行。比如说上面的例子,启动KGDB。 那么我们首先需要知道该command line从哪里传入kernel,这里看代码:
// drivers/of/fdt.c中
early_init_dt_scan
early_init_dt_scan_nodes
early_init_dt_scan_chosen
void __init early_init_dt_scan_nodes(void)
{
int rc;
/* Initialize {size,address}-cells info */
early_init_dt_scan_root();
/* Retrieve various information from the /chosen node */
//boot_command_line是一个装着cmdline的全局变量
rc = early_init_dt_scan_chosen(boot_command_line);
if (rc)
pr_warn("No chosen node found, continuing without\n");
/* Setup memory, calling early_init_dt_add_memory_arch */
early_init_dt_scan_memory();
/* Handle linux,usable-memory-range property */
early_init_dt_check_for_usable_mem_range();
}
int __init early_init_dt_scan_chosen(char *cmdline)
{
......
node = fdt_path_offset(fdt, "/chosen"); //寻找设备树chosen节点
if (node < 0)
node = fdt_path_offset(fdt, "/chosen@0");
if (node < 0)
/* Handle the cmdline config options even if no /chosen node */
goto handle_cmdline;
chosen_node_offset = node;
early_init_dt_check_for_initrd(node); //检查initrd文件的位置是否与dts一致
early_init_dt_check_for_elfcorehdr(node);//检查elfcorehdr节点
rng_seed = of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "rng-seed", &l);
if (rng_seed && l > 0) {
add_bootloader_randomness(rng_seed, l);
/* try to clear seed so it won't be found. */
fdt_nop_property(initial_boot_params, node, "rng-seed");
/* update CRC check value */
of_fdt_crc32 = crc32_be(~0, initial_boot_params,
fdt_totalsize(initial_boot_params));
}
/* Retrieve command line */
p = of_get_flat_dt_prop(node, "bootargs", &l);
if (p != NULL && l > 0)
strscpy(cmdline, p, min(l, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE));//解析bootarg部分参数
handle_cmdline:
/*
* CONFIG_CMDLINE is meant to be a default in case nothing else
* managed to set the command line, unless CONFIG_CMDLINE_FORCE
* is set in which case we override whatever was found earlier.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_CMDLINE
#if defined(CONFIG_CMDLINE_EXTEND)
strlcat(cmdline, " ", COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
strlcat(cmdline, CONFIG_CMDLINE, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
#elif defined(CONFIG_CMDLINE_FORCE)
strscpy(cmdline, CONFIG_CMDLINE, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
#else
/* No arguments from boot loader, use kernel's cmdl*/
// 将配置文件的CONFIG_CMDLINE设置的字符加入cmdline
if (!((char *)cmdline)[0])
strscpy(cmdline, CONFIG_CMDLINE, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
#endif
#endif /* CONFIG_CMDLINE */
pr_debug("Command line is: %s\n", (char *)cmdline);
return 0;
}上面可以看到,这里仅仅从设备树以及CONFIG_CMDLINE部分加入到cmdline中。我们这里不再讨论cmdline的形成过程,仅仅讨论early_param的机制。
在内核开始时:
// init/main.c
asmlinkage __visible void __init __no_sanitize_address start_kernel(void)
{
......
setup_arch(&command_line);
......
}
// arch/arm64/kernel/setup.c
void __init __no_sanitize_address setup_arch(char **cmdline_p)
{
......
parse_early_param();
......
}
// init/main.c
/* Arch code calls this early on, or if not, just before other parsing. */
void __init parse_early_param(void)
{
static int done __initdata;
static char tmp_cmdline[COMMAND_LINE_SIZE] __initdata;
if (done)
return;
/* All fall through to do_early_param. */
strscpy(tmp_cmdline, boot_command_line, COMMAND_LINE_SIZE);
parse_early_options(tmp_cmdline);
done = 1;
}
void __init parse_early_options(char *cmdline)
{
parse_args("early options", cmdline, NULL, 0, 0, 0, NULL,
do_early_param);
}
/* Check for early params. */
static int __init do_early_param(char *param, char *val,
const char *unused, void *arg)
{
const struct obs_kernel_param *p;
for (p = __setup_start; p < __setup_end; p++) {
if ((p->early && parameq(param, p->str)) ||
(strcmp(param, "console") == 0 &&
strcmp(p->str, "earlycon") == 0)
) {
if (p->setup_func(val) != 0)
pr_warn("Malformed early option '%s'\n", param);
}
}
/* We accept everything at this stage. */
return 0;
}上面的parse_args函数:
// kernel/params.c
char *parse_args(const char *doing,
char *args,
const struct kernel_param *params,
unsigned num,
s16 min_level,
s16 max_level,
void *arg,
int (*unknown)(char *param, char *val,
const char *doing, void *arg))
{
/*这里按照上下文,参数如下:
* doing = "early options"
* args = cmdline
* params = NULL
* num = 0
* min_level = 0
* max_level = 0
* arg = NULL
* unknown = do_early_param
*/
char *param, *val, *err = NULL;
/* Chew leading spaces */
args = skip_spaces(args); //删除cmdline开头的空格
......
while (*args) { //循环处理参数中的每个项目
int ret;
int irq_was_disabled;
args = next_arg(args, ¶m, &val);
/* Stop at -- */
if (!val && strcmp(param, "--") == 0) //结束符在"--"
return err ?: args;
irq_was_disabled = irqs_disabled();//记录下irq状态
ret = parse_one(param, val, doing, params, num,
min_level, max_level, arg, unknown);//解析一个项目
if (irq_was_disabled && !irqs_disabled())
pr_warn("%s: option '%s' enabled irq's!\n",
doing, param);
switch (ret) {//根据解析结果打印提示
case 0:
continue;
case -ENOENT:
pr_err("%s: Unknown parameter `%s'\n", doing, param);
break;
case -ENOSPC:
pr_err("%s: `%s' too large for parameter `%s'\n",
doing, val ?: "", param);
break;
default:
pr_err("%s: `%s' invalid for parameter `%s'\n",
doing, val ?: "", param);
break;
}
err = ERR_PTR(ret);
}
return err;
}继续看函数parse_one:
// kernel/params.c
static int parse_one(char *param,
char *val,
const char *doing,
const struct kernel_param *params,
unsigned num_params,
s16 min_level,
s16 max_level,
void *arg,
int (*handle_unknown)(char *param, char *val,
const char *doing, void *arg))
{
/*这里按照上下文,参数如下:
* param = <条目名>
* val = <条目值>
* doing = "early options"
* args = cmdline
* params = NULL
* num_params = 0
* min_level = 0
* max_level = 0
* arg = NULL
* unknown = do_early_param
* 比如你的cmdline有:kgdboc_earlycon=ttyFIQ0,115200
* 那么:
* 条目名 = kgdboc_earlycon
* 条目值 = ttyFIQ0,115200
*/
unsigned int i;
int err;
/* Find parameter */
for (i = 0; i < num_params; i++) {//只循环一次
if (parameq(param, params[i].name)) {//比较项目名称是否相同他,由于params为空,结果必然是false
if (params[i].level < min_level
|| params[i].level > max_level)
return 0;
/* No one handled NULL, so do it here. */
if (!val &&
!(params[i].ops->flags & KERNEL_PARAM_OPS_FL_NOARG))
return -EINVAL;
pr_debug("handling %s with %p\n", param,
params[i].ops->set);
kernel_param_lock(params[i].mod);
if (param_check_unsafe(¶ms[i]))
err = params[i].ops->set(val, ¶ms[i]);
else
err = -EPERM;
kernel_param_unlock(params[i].mod);
return err;
}
}
if (handle_unknown) {//处理参数,开始回调early_param设置的函数
pr_debug("doing %s: %s='%s'\n", doing, param, val);
return handle_unknown(param, val, doing, arg); //执行do_early_param函数
}
pr_debug("Unknown argument '%s'\n", param);
return -ENOENT;
}我们继续看看do_early_param:
// init/main.c
/* Check for early params. */
static int __init do_early_param(char *param, char *val,
const char *unused, void *arg)
{
const struct obs_kernel_param *p;
for (p = __setup_start; p < __setup_end; p++) {//遍历section-".init.setup"中的参数
//如果名字相等,并且设置了early=1,则可以执行回调
// 或者,该项目(cmdline一部分)为:"console"且early_param中的str为"earlycon"
if ((p->early && parameq(param, p->str)) ||
(strcmp(param, "console") == 0 &&
strcmp(p->str, "earlycon") == 0)
) {
if (p->setup_func(val) != 0)
pr_warn("Malformed early option '%s'\n", param);
}
}
/* We accept everything at this stage. */
return 0;
}好的我们来解释一下上面的过程,我们通过分解cmdline为一个个单独的项目,每个项目与所有的early_param声明进行比较,如果cmdline有该名字,则表示激活early_param定义的回调函数。当然这里的consol比较特殊,这里不作分析。
我们以上面的early_param("kgdboc_earlycon", kgdboc_earlycon_init);分析,如果cmdlibne为:
Kernel command line: storagemedia=emmc androidboot.storagemedia=emmc androidboot.mode=normal kgdboc_earlycon=uart androidboot.verifiedbootstate=orange rw rootwait earlycon=uart8250,mmio32,0xfeb50000 console=ttyFIQ0 irqchip.gicv3_pseudo_nmi=0 root=PARTUUID=614e0000-0000其中就包含了kgdboc_earlycon=uart,并且early_param被编译到系统中(也就是开启了KGDB功能),那么就会执行函数kgdboc_earlycon_init。 **注意**:有些就版本会让你使用kgdboc=ttyFIQ0,115200 kgdbwait进入KGDB,但是我发现新的内核并不支持该写法,现在需要使用kgdboc_earlycon=uart`来进入。